Brownout vs Blackout: Key Differences
Picture this: you’re in the middle of something important when suddenly, the lights flicker and fade. It’s a scenario we all know too well.
Power outages can disrupt our daily lives and leave us feeling helpless. Understanding the critical differences between two common power-related issues – brownouts and blackouts – can empower you to take proactive measures and minimize inconveniences.
“What exactly is a brownout? Is it comparable to a blackout, or do they exhibit distinct differences?”

Blackouts and brownouts signify abrupt power disruptions, but they carry subtle distinctions. While a blackout entails the total loss of power, a brownout denotes a partial power reduction. In the case of a brownout, electricity is still supplied, albeit at a lower voltage level.
To ensure warmth and comfort during power interruptions, utilizing Vigorpool Solar Generators is highly recommended. These generators can charge all your appliances and be dependable backup power solutions.
Blackouts and brownouts signify abrupt power disruptions, but they carry subtle distinctions. While a blackout entails the total loss of power, a brownout denotes a partial power reduction. In the case of a brownout, electricity is still supplied, albeit at a lower voltage level.
To ensure warmth and comfort during power interruptions, utilizing Vigorpool Solar Generators is highly recommended. These generators can charge all your appliances and be dependable backup power solutions.
What Is A Brownout?
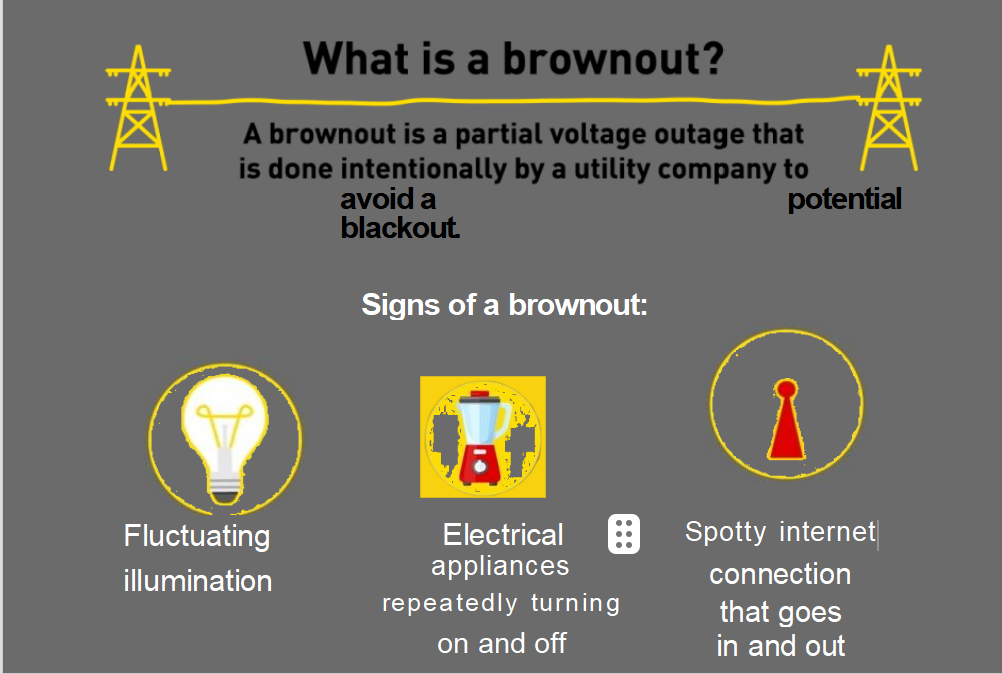
Brownouts: A brownout materializes as a reduction in voltage within an electrical power system. Frequently stemming from heightened demand or technical glitches within the power network, brownouts prompt dimming of lights, erratic electronic device behavior, and diminished appliance performance. The repercussions of brownouts encompass potential damage to electronic equipment, thereby shortening their operational longevity.
What Is A Blackout?

What is a blackout?
A blackout signifies an utter power failure. In contrast to the deliberate nature of a brownout, a blackout arises entirely without warning. An array of factors can trigger a blackout, encompassing:
- Damaged electrical lines
- Lightning striking electrical poles
- Ice on power lines
- Fallen tree branches on power lines
- A spike in power demand that pushes the grid past its limit
- An earthquake that damaged power lines
- A vehicle that collided with a utility pole
- Severe weather
Blackouts: A blackout constitutes the total cessation of power distribution within a specific region. Diverse catalysts can initiate an outage, ranging from adverse weather phenomena to equipment malfunctions and system overloads. Blackouts prompt an abrupt and comprehensive halt in electrical supply, affecting residences, commercial establishments, and public amenities. Their duration can vary, from brief moments to prolonged stretches, contingent upon the underlying cause and the efficiency of restoration endeavors.
Causes and Effects
Brownouts: Brownouts often occur during periods of high demand for electricity, such as hot summer days when air conditioners are running at full blast. Additionally
Blackouts: Blackouts can stem from natural disasters like hurricanes, earthquakes, or severe storms, as well as manufactured factors like equipment malfunctions or accidents. The effects of blackouts are more powerful, encompassing a complete halt in electrical services. Homes lose heating, cooling, lighting, and refrigeration, while businesses face disruptions to operations and financial losses.
Prevention and Preparedness
Brownouts: Mitigating brownouts involves adopting energy-efficient appliances and habits. Disperse your electricity consumption across the day, refrain from operating numerous high-power gadgets concurrently, and verify the compliance of your wiring and electrical setups with established standards. Incorporating voltage stabilizers can effectively modulate incoming power, safeguarding your electronic devices in the process.
Blackouts: The cornerstone of addressing blackouts is readiness. Formulate an emergency kit encompassing vital provisions like flashlights, batteries, non-perishable sustenance, and a first-aid package. Contemplate procuring a backup generator to furnish interim power during extended interruptions. Maintain a consistent regimen of inspecting and upkeeping your generator to ascertain its optimal functionality when needed.
What actions should I take if faced with an electrical brownout or blackout?
In the event of a brownout or blackout, remain composed. In the case of an abrupt power loss, prioritize the safe unplugging of electronic devices. Subsequently, contact your local utility company to ascertain whether the problem originates from your electrical grid. If the utility company verifies the system’s regular operation, potential isolated issues within your residence might be at play. In such situations, it’s advisable to engage an electrician for assistance—avoid personally investigating the outage to mitigate potential safety hazards.
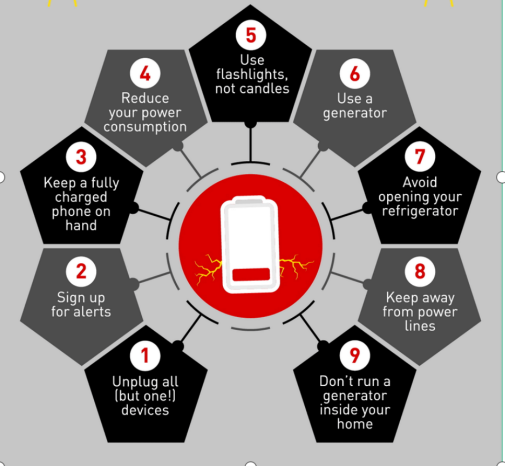
Upon verification of a grid issue by your utility company, adhere to the following guidelines:
1. Unplug all of your devices
2. Sign up for alerts
3. Keep a fully charged phone on hand
4. Reduce your power consumption
5. Use flashlights, not candles
6. Use a generator
7. Avoid opening your refrigerator
8. Keep away from power lines
9. Don’t run a generator inside your home
Which devices are susceptible to power failures? Numerous devices are at risk of damage during power failures, whether blackouts or brownouts cause them. Some of the electrical devices that can experience damage due to power failures include:
- Computers
- Refrigerators
- Landline phones
- Microwaves
- Ovens
- Clocks
- Lamps
- Hair dryers
- Washer/Dryer
- Toaster
- Coffee machine
In essence, any device linked to an outlet or power strip faces susceptibility to power failures. However, devices incorporating electric motors or components are particularly vulnerable to brownouts. This vulnerability arises due to the potential of low voltage to induce heightened current draw and subsequent overheating in such devices. Exposure to a voltage lower than the norm increases the likelihood of damage to electric motors and components.
During the occurrence of either a blackout or a brownout, it is advisable to disconnect these devices to avert potential damage from power surges, which can manifest when electricity is restored.
How do I protect my appliances from brownouts?
Specific measures should be taken to safeguard your appliances and stave off potential damage when confronted with a brownout scenario.
First and foremost, it’s imperative to unplug all your devices. Even though some devices might still function during a brownout, erring caution by opening everything is advisable. Doing so will avert the risk of exposing your devices to irregular electrical currents that could result in damage. Moreover, during this period, making an effort to curtail your overall power consumption is wise, as the brownout typically stems from a sudden surge in power usage.
An alternative option is to employ an Undervoltage relay, automatically disconnecting your devices when the voltage dips below a certain threshold. However, it’s worth noting that these relays can be costly and are primarily recommended for susceptible appliances like LCD TVs and computers.
An additional solution is to utilize an uninterruptible power supply (UPS). A UPS has voltage regulation capabilities, ensuring a consistent voltage output even when the supplied voltage fluctuates. This feature proves valuable during brownouts, as it guarantees a steady power supply for critical devices.
Learn about the UPS functions and technical demonstrations of VigorPool CAPTAIN Series products: How to use Captain 1200 as a UPS?

Employing a power strip or surge protector is also a viable strategy to shield your devices from low voltage. A surge protector effectively safeguards anything plugged into it during a blackout, making it prudent to allocate it for your high-value or frequently used devices.
A final preventative measure involves scheduling an annual electrical assessment. A yearly electrical walkthrough validates proper wiring and modernized electrical systems, effectively preempting surges from transpiring. Undertaking an electrical walkthrough is a reliable means to ensure the safety of your household and property during a brownout scenario.
Staying Safe
How can I safeguard my appliances against brownouts?
In the event of a brownout, there are several steps you can take to shield your appliances and prevent potential damage:
1. Unplug all your devices
When a brownout occurs, it’s advisable to unplug all your appliances. This action helps minimize the risk of damage resulting from voltage fluctuations when power is restored.
- Employ an undervoltage relay:
Implementing an undervoltage relay can be beneficial. This mechanism disconnects your appliances when the voltage drops below a predetermined threshold, safeguarding them from low voltage situations.
- Utilize an uninterruptible power supply (UPS):
Opting for an uninterruptible power supply ensures a consistent and stable power source for your critical devices, even during brownouts. This extra layer of protection helps prevent potential harm due to voltage fluctuations.
- Install surge protectors:
By employing surge protectors, you can shield your electronics from harm caused by low voltage conditions during brownouts. These devices help regulate the voltage and prevent sudden surges when power is reinstated.
- Seek the expertise of an electrician for an annual electrical assessment:
To enhance overall electrical safety, consider enlisting the services of an electrician for an annual inspection. This professional assessment can identify potential vulnerabilities in your electrical system, enabling you to address any issues proactively.
Brownouts: In the event of a brownout, it’s advisable to disconnect sensitive electronics to forestall potential damage during power restoration. Employ surge protectors to shield devices such as computers, televisions, and gaming consoles. These precautions effectively counteract the risk of power surges causing harm to your equipment.
Blackouts: When confronted with a faint, make safety paramount by opting for flashlights instead of candles to avert potential fire risks—power down all significant appliances to thwart abrupt power surges during the restoration process. If utilizing a generator, position it outdoors to prevent the buildup of carbon monoxide.
Concluding Remarks
Navigating a loss of electrical power can undoubtedly be an unsettling experience. The sudden shift can trigger apprehension, whether facing a complete blackout or a partial reduction in force. In an instant, the familiar hum of appliances can fade into darkness, leaving an eerie atmosphere.
Nonetheless, it’s vital to resist the urge to panic when confronted with a blackout or brownout. Despite the unsettling nature of the situation, maintaining a composed demeanor is crucial to take appropriate actions for your safety. Commence by unplugging electronic devices, minimizing power consumption, relying on flashlights for illumination, and steering clear of power lines. These simple guidelines will significantly improve your safety during a brownout or blackout.
While both situations can provoke unease, understanding the differences between brownouts and blackouts is crucial for a tailored response. With accurate knowledge, you can mitigate potential damage to your appliances and navigate the power outage until electricity is restored.


